Search engines are computer programs to find answers to queries in a collection of information, which might be a library catalog or a database but is most commonly the World Wide Web. A Web search engine produces a list of “pages”—computer files listed on the Web—that contain or relate to the terms in a query entered by the user into a search bar field. Most search engines allow the user to join tours with such qualifiers as and, or, and not to refine queries. They may also search specifically for images, videos, phrases, questions, news articles, or names of websites.
Table of Contents
How Do Search Engines Work?
Google is the most commonly used internet search engine. Google search takes place in the following three stages:
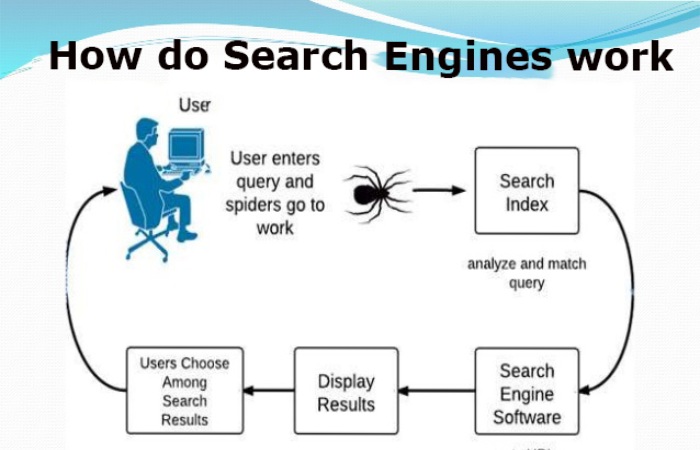
Crawling
Crawlers discover what pages exist on the Web. A search engines constantly looks for new and updated pages to add to its list of known pages. It is referred to as URL discovery. Once a page is discovered, the crawler examines its content. Search engine uses an algorithm to select which pages to crawl.
Indexing
Once the page is crawled, the textual content is administered, examined, and labelled with characteristics and metadata that help the search engine comprehend what the content is about. This also enables the search engine to weed out duplicate pages and collect signals about the content, such as the country or region the page is local to and the usability of the page.
Searching and ranking
When a user arrives at a query, the search engine searches the index for matching pages and returns the most relevant results on the search engine results page (SERP). The engine rank content on several factors, such as the page’s authoritativeness, backlinks, and keywords a page contains.
Specialized content search engines are more selective about the parts of the Web they crawl and index. For example, Creative Commons Search is a search engine for content shared explicitly for reuse under the Creative Commons license. This search engine only looks for that specific type of content.
What is A Search Engine Algorithm?
SEO is a term used to explain a complex algorithm system that evaluates all indexed pages and decides which ones should look in the search results for a given request.
For example, the Google algorithm uses lots of factors (many of which are well known, while some are kept secret) in different parts, such as:
- Meaning of the query (know what the user meant with the exact words they used, the search intent, etc.)
- Page relevancy (the search engine needs to know if the page answers your search query)
- Content quality (Algorithms determine whether web pages are a great source of information based on internal and external factors; sum and quality of backlinks are important factors here)
- Usability of the page (consider webpage quality from a technical point of view: responsiveness, page speed, security, etc.)
What are the most popular search engines?
Although there are several search engines worldwide, only a rare of them control the overall search engine market and remain prevalent due to their quality, usefulness, etc.
- Yahoo!
- Microsoft Bing
- Baidu
- Yandex
Search Engine Optimization
In addition to providing valuable data to their users, search engines can also help brands help their websites.
Improving your website for relevant search queries is essential to any internet marketing strategy, as it can generate more traffic to your web pages.
All the performance and techniques website owners do to improve their rankings in search are called search engine optimization (SEO).
If we want to simplify SEO, we can say that everything revolves around the three most important factors:
- Technical improvement
- Great content
- High-quality backlinks
How Do Search Engines Make Money?
The critical source of income for search engines like Google comes from various indirect sources. Search engines can monetize your services through:
Advertising
Google uses its advertising service called Google Ads, which can help brands show their products in the search results, and in return, it gets a small commission every time a user clicks on the advertisement.
Online Shopping
Search engines can help various products in their optimized search results. If the user clicks through or buys a product, the search engines will take a small percentage of the purchase.
Services
Google embeds its services (e.g., Play Store, Google Apps, Google Cloud, etc.) with its search engine and thus generates revenue through customers who use them.

